Design & Technology
Hospitality & Catering
The discovery of a new dish contributes more to the happiness of mankind than the discovery of a star.
– Jean Anthelme Brillat-Savarin
Food Technology, Hospitality & Catering Curriculum Intent Statement
At Looe Community Academy, our Food curriculum is designed to nurture curiosity, deepen understanding, and empower every learner to engage creatively and critically with the world of food. We believe that knowledge is connected, not fragmented, so our curriculum builds meaningful links between practical skills, nutrition, sustainability, and cultural heritage, enabling students to see patterns and purpose in what they learn and cook.
Central to our curriculum are the big ideas of Safety, Food Skills, Nutri prep, and Food Future. These concepts underpin every unit, helping students explore how food choices shape health, identity, and the environment. Through these lenses, learners develop confidence in the kitchen, mastery of essential techniques, and the ability to make informed decisions about what they eat and why.
We aim to provide high challenge with low threat, creating a culture where students feel safe to take creative risks, experiment with flavours, and develop independence. Through rich encounters with diverse cuisines—from global dishes to local seafood traditions—students learn to question, interpret, and innovate. They study nutrition and dietary needs, explore ethical and sustainable food practices, and connect their learning to real-world hospitality and catering opportunities.
Our curriculum prioritises practical competence, cultural understanding, and academic depth. Students learn the craft of cooking while developing curiosity through sensory analysis, food provenance, and links to science and geography. They are encouraged to ask questions, make connections, and express themselves through creative dishes, preparing them for life beyond the classroom.
Ultimately, our intent is to ignite a lifelong passion for food, equipping students with the skills, knowledge, and creativity to thrive as thoughtful cooks, informed consumers, and innovative professionals in an ever-changing world.
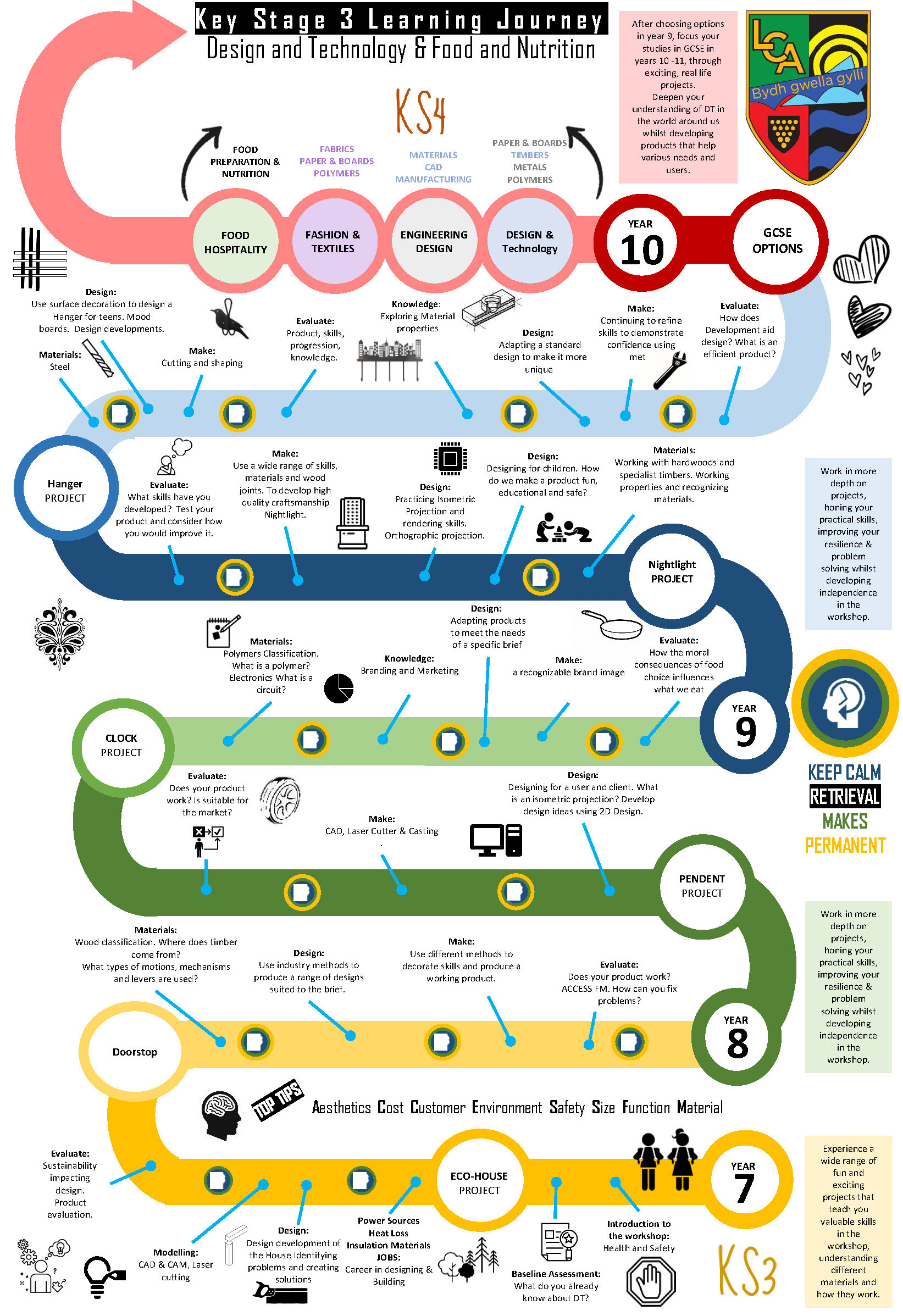
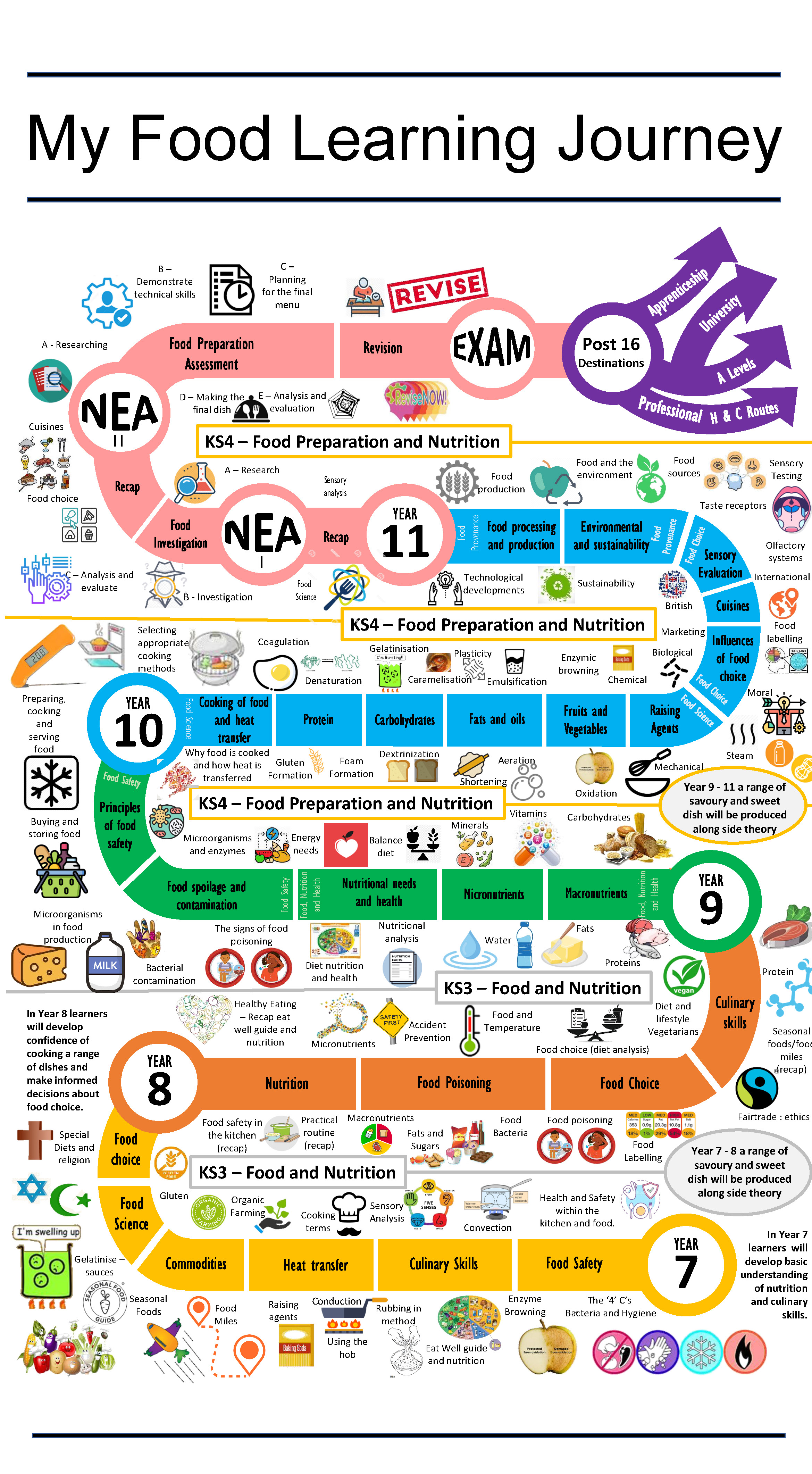
Progression from Key Stage 3 to Key Stage 4
Our curriculum is spiralled and challenging, revisiting key concepts at increasing levels of complexity:
-
Key Stage 3: Students begin with the foundations—safe working practices, hygiene, and basic food preparation. They learn essential knife skills, simple recipes, and the principles of healthy eating. As they progress, they explore global cuisines, local food heritage, and sustainability, applying nutritional knowledge to create balanced meals. They also develop an understanding of allergens, dietary needs, and cultural food preferences.
-
Key Stage 4: Challenge deepens as students master advanced cooking techniques and apply theory to practice. They study hospitality and catering in depth, including menu planning, food presentation, and customer service. Learners engage with industry standards, ethical sourcing, and sustainability, while developing entrepreneurial skills and exploring career pathways. Written analysis, evaluation, and practical assessments prepare students for GCSE success and future opportunities in the food and hospitality sector.
Curriculum Pathways
Additional Opportunities Beyond the Classroom
- Fish mongers and farmers
- Local AA chefs
- Sustainable living
- Navy involvement
- Catering for events
- Aumni Daniel Lewis Cfe in Plymouth
Design & Technology
Good buildings come from good people, and all problems are solved by good design.
- Stephen Gardiner
Design & Technology Curriculum Intent Statement
At Looe Community Academy, our Design & Technology curriculum is designed to nurture curiosity, deepen understanding, and empower every learner to think creatively and critically about the world of design. We believe that knowledge is connected, not fragmented, so our curriculum builds meaningful links between investigation, design, development, making, and evaluation, enabling students to see patterns and purpose in what they create.
Central to our curriculum are the big ideas of Investigate, Design, Develop, Make, and Evaluate. These concepts underpin every project, helping students explore how products are conceived, refined, and manufactured to meet human needs. Through these lenses, learners develop technical precision, problem-solving skills, and the ability to innovate responsibly.
We aim to encourage learners to take creative risks, experiment with materials, and develop independence. Through rich encounters with traditional craftsmanship and modern technologies—from hand tools and finger joints to CAD/CAM and smart materials—students learn to question, interpret, and innovate. They study sustainability, ergonomics, and the work of influential designers, connecting their learning to real-world applications and future careers.
Our curriculum prioritises technical skill, creative independence, and academic depth. Students learn the craft of making while developing curiosity through material science, design strategies, and iterative thinking. They are encouraged to ask questions, make connections, and express themselves through purposeful design, preparing them for life beyond the classroom.
Ultimately, our intent is to ignite a lifelong passion for design, equipping students with the skills, knowledge, and creativity to thrive as thoughtful makers, problem-solvers, and innovators in an ever-changing world.
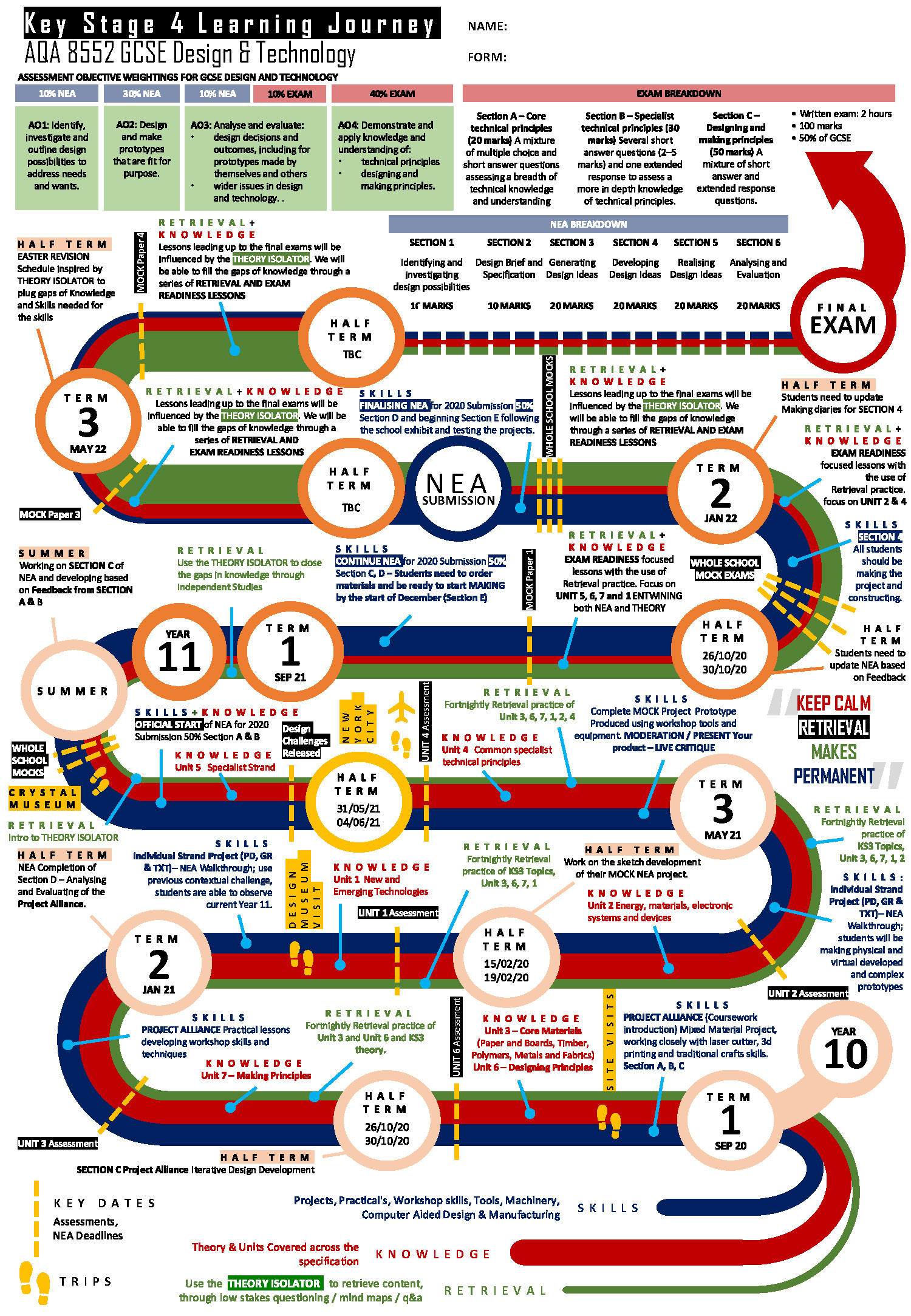
Progression from Key Stage 3 to Key Stage 4
Our curriculum is spiralled and challenging, revisiting key concepts at increasing levels of complexity:
-
Key Stage 3: Students begin with the foundations—safe working practices, risk assessment, and basic hand tool skills. They learn to investigate briefs, analyse products, and create simple prototypes using wood, acrylic, and basic electronics. CAD/CAM is introduced alongside traditional techniques, building confidence in digital and physical making.
-
Key Stage 4: Challenge deepens as students master advanced design strategies and manufacturing processes. They explore new and emerging technologies, sustainability, and ethical design. Learners develop iterative design thinking, produce detailed working drawings, and apply tolerances and quality control. Projects integrate CAD/CAM, electronics, and material science, preparing students for GCSE assessment and future careers in engineering, product design, and creative industries.
Textiles
In the world of textiles, every thread tells a story.
– Unknown
Textiles Curriculum Intent Statement
During the Art - Textiles course, the students will explore a variety of textile techniques ranging from weaving, knitting, hand appliquéing, machine embroidery, print and dyeing techniques. While they consider elements, such as colour, line, texture, pattern, shape, composition, structure and form.
During KS3 the students have a year theme such as: Cornish coastal path, Colours & patterns of India or based on an artist. They work through the theme and create a finished piece. The lessons are guided and varied to ensure that every student can succeed.
During KS4 the students deep dive into the world of textiles with a more detailed look at artists, designers and art movements for stimulus and context. They will visit galleries and locations relevant to their theme.
They are encouraged to take creative risks and learn through mistakes, as well as enjoy and include happy accidents by self-reflection and refinement.
They may present their outcome as a functional or non-functorial outcome such as a wall hanging, cushion cover, textile sculpture or garment.
Students develop their abilities to draw and then create patterns to work from. They grow in confidence through being guided through creating mini-experimental outcomes before finally producing personal independent responses.
Focused Curriculum Contextual Routines
- Visualiser
- Reading
- Independent develop
- Peer learning through – turn and talk
- Modelling
Additional Opportunities Beyond the Classroom
- Links with Plymouth University
- Textiles industry and fashion
- The students exhibit their work alongside Art students at local galleries
Curriculum Pathways